NLP-Connecting Language to the World
- connect vision - language
- generative vision-language model
- others[speech, audio]
- from language to code
- from language to action
1.connect vision - language
History
1960s first cv project.
2000s shallow classifiers and feature engineering.
2012 deep learning revolution.
CNN in ImageNet.
unification of architectures.
Rise of image generation (VAEs, GANs, etc.).
2020s eras of vision transformer.
How to encode images?
Vision Transformers (ViT). Image to patch(matrices, e.g. you have different channels for different colors) + position embedding. Feed these channels into transformers.
How to encode paired image-text?
Idea: create a space to represent both semantics of language and image. (This is similar to the idea while I use Meta’s laser_encoders to complete multilingual tasks).
Then create a model that can align semantically-equivalent text and images nearby.
把image和text转到同一个坐标系里,相关度高的图片和文字如猫猫图片+“A cat”,在坐标系里就会离得近。
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP)
Having two encoders: text encoder, image encoder. Having a function $F$, for every text and image pair, if they are align, then $F=1$, if they are not align, $F$ is close to zero.
In CLIP, the description is for the whole image, not partial image.
Tasks CLIP can do: classification. it gives probabilities of things.
Demo: gives an image of JHU campus, gives several keywords: Johns Hopkins, Stanford, Berkeley, UPenn. CLIP assign Johns Hopkins with highest probabilities.
No generation capabilities; Prompting / In-Context Learning: Few-shot captioning.
What happened after CLIP?
- Data scaling up
- Model design
- Objective functions(e.g. Contrastive learning)
Open source model: OpenCLIP.
Pre-training on LAION-5B dataset.
2.generative vision-language model
Image Generation Toolkit
Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN): have discriminator to notice fake or real images.
Auto-regressive(AR):识别追踪算法
Non-AR Transformer
Difussion: add noise and then denoising.
Diffusion models
Intuition: generate images in one path, step-by-step manner. Add noise to the image, until it is randomly noisy, then based on the labels, do the reverse sampling process to denoise the noisy images.
Text to Image Generation
DALL-E.
Based on CLIP.
A text prompt is imput into a text encoder that is trained to map the prompt to a representation space.
它主要包括三个部分:CLIP,先验模块prior和img decoder。其中CLIP又包含text encoder和img encoder。
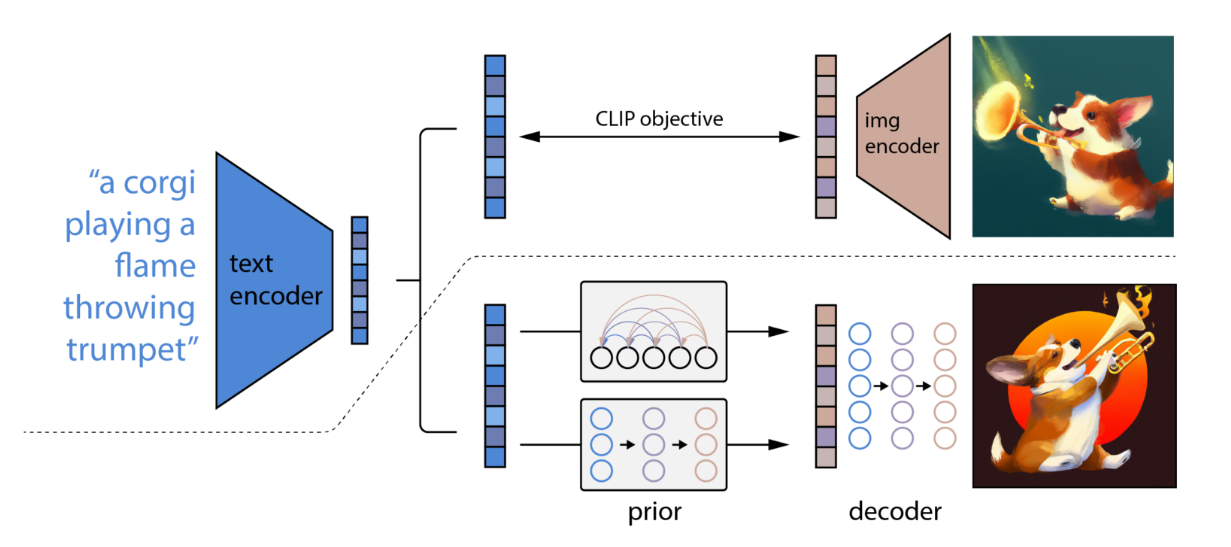
Imagen.
Simpler than DALL-E.
Frozen language model providing text embeddings to all diffusion models.
Text to Visual
text to video
text to 3D shapes(家装)
text to motions/navigations(动漫,游戏)
Multi-modal GPT4
strong zero-shot visual understanding and reasoning capability.
Image-to-Text Generative Models
Model architectures:
- Pre-trained image encoders
- Pre-trained language models
- Modules(to be trained) to connect the two modalities.
LLaVA model.
LLaVA architecture:
Provide language instructions. Turn these instructions into embeddings. At the same time, mapping images into embeddings that is understandable by the language model we will use. Under the help of CLIP image encoder and a projection matrix which will map the embedded image to the same dimension as the LLM input(linear projection).
The LM is fixed, pre-trained, the CLIP encoder is only trained with CLIP dataset, then it is still useful to train on it instead of fixing it.
LLaVA Training:
Step 1: Feature alignment — aligning the representation of Vision Encoder and LLM.
- Both Vision Encoder and LLM are kept frozen.
- The Only training parameter is W the projection matrix.
Step 2: End to end fine-tuning
- Vision Encoder is kept frozen. The trainig params are W and LLM.
Can also do Multimodal RLHF.
(End of lecture 21)




