2025 Spring
- Power BI Self-Project: PWC Call Center Visual
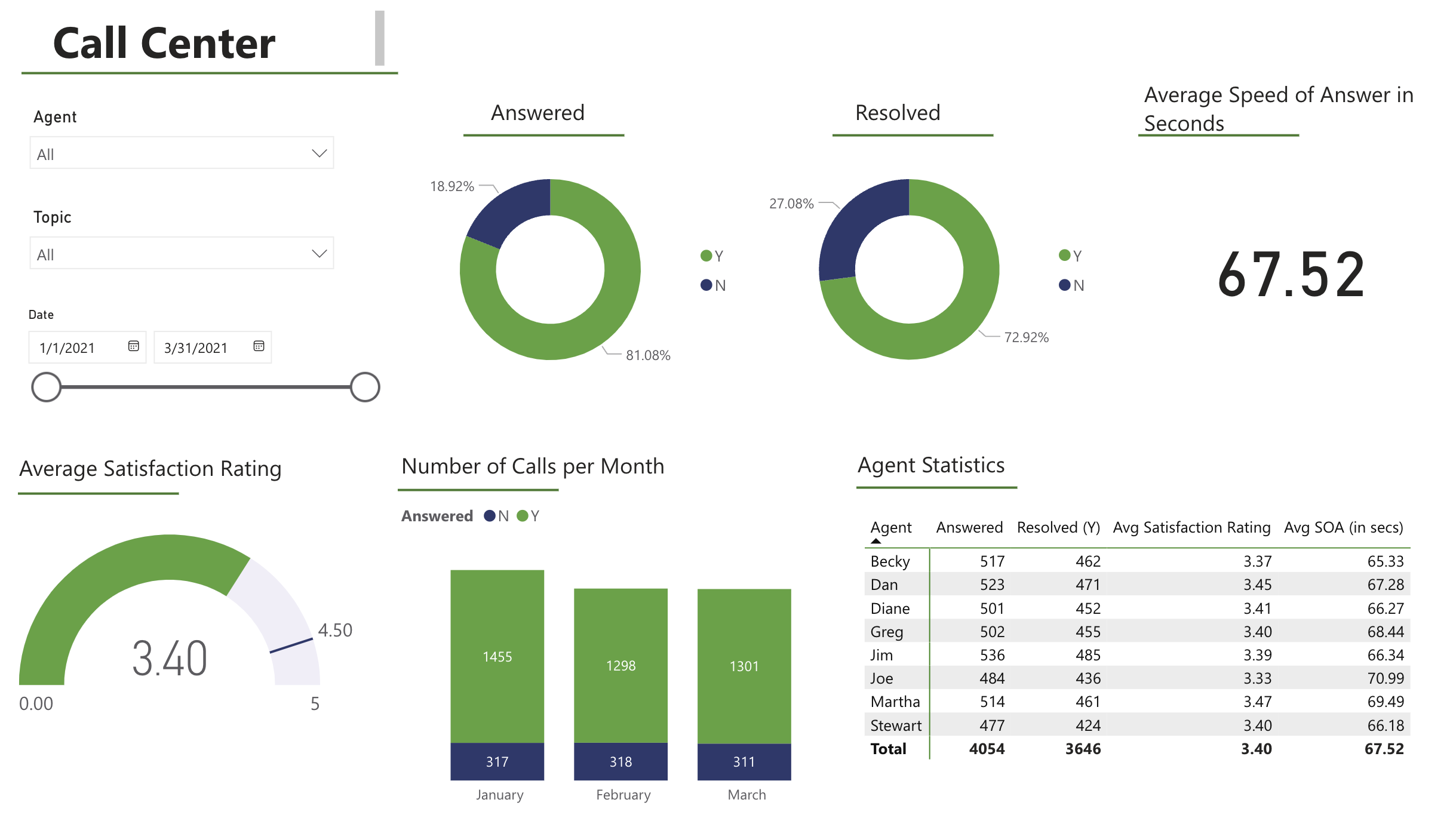
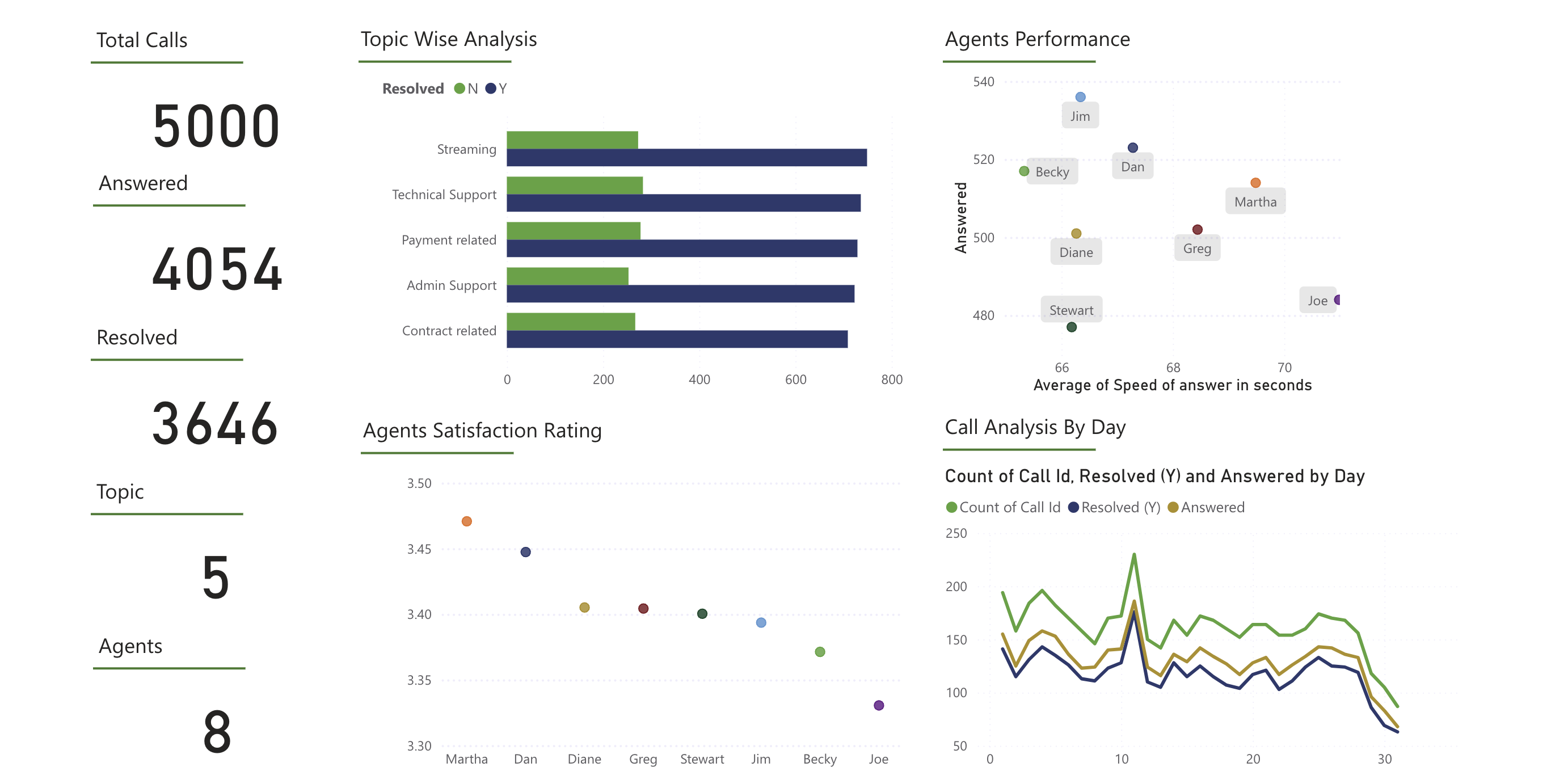
2024 Spring
Music Emotion Prediction Using Recurrent Neural Networks
Xinyu Chang, Xiangyu Zhang, Haoruo Zhang, Yulu Ran | paper | github
Abstract: This study explores the application of recurrent neural networks to recognize emotions conveyed in music, aiming to enhance music recommendation systems and support therapeutic interventions by tailoring music to fit listeners’ emotional states. We utilize Russell’s Emotion Quadrant to categorize music into four distinct emotional regions and develop models capable of accurately predicting these categories. Our approach involves extracting a comprehensive set of audio features using Librosa and applying various recurrent neural network architectures, including standard RNNs, Bidirectional RNNs, and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Initial experiments are conducted using a dataset of 900 audio clips, labeled according to the emotional quadrants. We compare the performance of our neural network models against a set of baseline classifiers and analyze their effectiveness in capturing the temporal dynamics inherent in musical expression. The results indicate that simpler RNN architectures may perform comparably or even superiorly to more complex models, particularly in smaller datasets. We’ve also applied the following experiments on larger datasets: one is augmented based on our original dataset, and the other is from other sources. This research not only enhances our understanding of the emotional impact of music but also demonstrates the potential of neural networks in creating more personalized and emotionally resonant music recommendation and therapy systems.MambaDiff: Revolutionizing Seq2Seq Models with Diffusion model and Mamba architecture
Guannan He, Xiangyu Zhang, Xinyu Chang | github
Abstract: In this work, we introduce MambaDiff, a novel architecture that integrates the strengths of diffusion models with the Mamba architecture to address the challenges faced in sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) modeling tasks. Traditional Seq2Seq models, while powerful, often struggle with maintaining contextual relevance and computational efficiency, especially over longer sequences. By leveraging the gradual refinement capabilities of diffusion models and the scalable, efficient processing of the Mamba architecture, MambaDiff aims to enhance the quality of generated text across extensive contexts significantly. We demonstrate the potential of our approach through diverse NLP tasks such as open-domain dialogue, question generation, text simplification, and paraphrasing. This paper will detail the motivation behind this integration, the theoretical and practical benefits, and preliminary results that highlight its effectiveness compared to existing models.
2023 Summer
- Elevator Optimization: Application of Spatial Process and Gibbs Random Field Approaches for Dumbwaiter Modeling and Multi-Dumbwaiter Systems
Zheng Cao, Benjamin Lu Davis, Wanchaloem Wunkaew, Xinyu Chang | paper
Abstract: This research investigates analytical and quantitative methods for simulating elevator optimizations. To maximize overall elevator usage, we concentrate on creating a multiple-user positive-sum system that is inspired by agent-based game theory. We define and create basic “Dumbwaiter” models by attempting both the Spatial Process Approach and the Gibbs Random Field Approach. These two mathematical techniques approach the problem from different points of view: the spatial process can give an analytical solution in continuous space and the Gibbs Random Field provides a discrete framework to flexibly model the problem on a computer. Starting from the simplest case, we target the assumptions to provide concrete solutions to the models and develop a “Multi-Dumbwaiter System”. This paper examines, evaluates, and proves the ultimate success of such implemented strategies to design the basic elevator’s optimal policy; consequently, not only do we believe in the results’ practicality for industry, but also their potential for application.




